Shall we always use [unowned self] inside closure in Swift
SwiftAutomatic Ref-CountingSwift Problem Overview
In WWDC 2014 session 403 Intermediate Swift and transcript, there was the following slide

The speaker said in that case, if we don't use [unowned self] there, it will be a memory leak. Does it mean we should always use [unowned self] inside closure?
On line 64 of ViewController.swift of the Swift Weather app, I don't use [unowned self]. But I update the UI by using some @IBOutlets like self.temperature and self.loadingIndicator. It may be OK because all @IBOutlets I defined are weak. But for safety, should we always use [unowned self]?
class TempNotifier {
var onChange: (Int) -> Void = {_ in }
var currentTemp = 72
init() {
onChange = { [unowned self] temp in
self.currentTemp = temp
}
}
}
Swift Solutions
Solution 1 - Swift
No, there are definitely times where you would not want to use [unowned self]. Sometimes you want the closure to capture self in order to make sure that it is still around by the time the closure is called.
Example: Making an asynchronous network request
If you are making an asynchronous network request you do want the closure to retain self for when the request finishes. That object may have otherwise been deallocated but you still want to be able to handle the request finishing.
When to use unowned self or weak self
The only time where you really want to use [unowned self] or [weak self] is when you would create a strong reference cycle. A strong reference cycle is when there is a loop of ownership where objects end up owning each other (maybe through a third party) and therefore they will never be deallocated because they are both ensuring that each other stick around.
In the specific case of a closure, you just need to realize that any variable that is referenced inside of it, gets "owned" by the closure. As long as the closure is around, those objects are guaranteed to be around. The only way to stop that ownership, is to do the [unowned self] or [weak self]. So if a class owns a closure, and that closure captures a strong reference to that class, then you have a strong reference cycle between the closure and the class. This also includes if the class owns something that owns the closure.
Specifically in the example from the video
In the example on the slide, TempNotifier owns the closure through the onChange member variable. If they did not declare self as unowned, the closure would also own self creating a strong reference cycle.
Difference between unowned and weak
The difference between unowned and weak is that weak is declared as an Optional while unowned is not. By declaring it weak you get to handle the case that it might be nil inside the closure at some point. If you try to access an unowned variable that happens to be nil, it will crash the whole program. So only use unowned when you are positive that variable will always be around while the closure is around
Solution 2 - Swift
Update 11/2016
I wrote an article on this extending this answer (looking into SIL to understand what ARC does), check it out here.
Original answer
The previous answers don't really give straightforward rules on when to use one over the other and why, so let me add a few things.
The unowned or weak discussion boils down to a question of lifetime of the variable and the closure that references it.
Scenarios
You can have two possible scenarios:
-
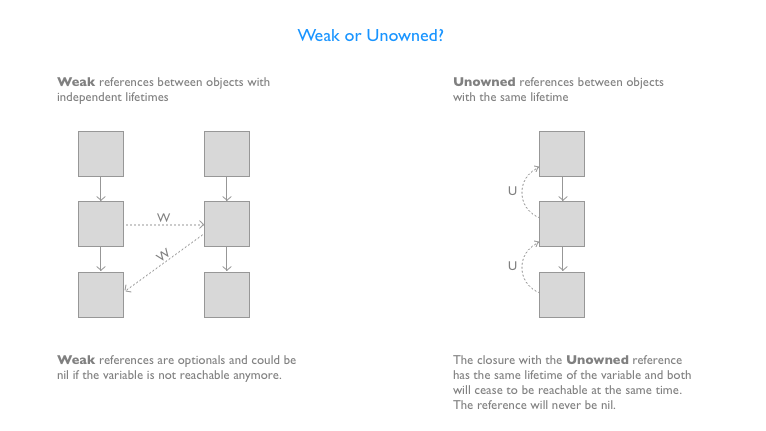
The closure have the same lifetime of the variable, so the closure will be reachable only until the variable is reachable. The variable and the closure have the same lifetime. In this case you should declare the reference as unowned. A common example is the
[unowned self]used in many example of small closures that do something in the context of their parent and that not being referenced anywhere else do not outlive their parents. -
The closure lifetime is independent from the one of the variable, the closure could still be referenced when the variable is not reachable anymore. In this case you should declare the reference as weak and verify it's not nil before using it (don't force unwrap). A common example of this is the
[weak delegate]you can see in some examples of closure referencing a completely unrelated (lifetime-wise) delegate object.
Actual Usage
So, which will/should you actually use most of the times?
Quoting Joe Groff from twitter:
> Unowned is faster and allows for immutability and nonoptionality. > > If you don't need weak, don't use it.
You'll find more about unowned* inner workings here.
* Usually also referred to as unowned(safe) to indicate that runtime checks (that lead to a crash for invalid references) are performed before accessing the unowned reference.
Solution 3 - Swift
I thought I would add some concrete examples specifically for a view controller. Many of the explanations, not just here on Stack Overflow, are really good, but I work better with real world examples (@drewag had a good start on this):
-
If you have a closure to handle a response from a network requests use
weak, because they are long lived. The view controller could close before the request completes soselfno longer points to a valid object when the closure is called. -
If you have closure that handles an event on a button. This can be
unownedbecause as soon as the view controller goes away, the button and any other items it may be referencing fromselfgoes away at the same time. The closure block will also go away at the same time.class MyViewController: UIViewController { @IBOutlet weak var myButton: UIButton! let networkManager = NetworkManager() let buttonPressClosure: () -> Void // closure must be held in this class. override func viewDidLoad() { // use unowned here buttonPressClosure = { [unowned self] in self.changeDisplayViewMode() // won't happen after vc closes. } // use weak here networkManager.fetch(query: query) { [weak self] (results, error) in self?.updateUI() // could be called any time after vc closes } } @IBAction func buttonPress(self: Any) { buttonPressClosure() } // rest of class below. }
Solution 4 - Swift
If self could be nil in the closure use [weak self].
If self will never be nil in the closure use [unowned self].
The Apple Swift documentation has a great section with images explaining the difference between using strong, weak, and unowned in closures:
Solution 5 - Swift
Here is brilliant quotes from Apple Developer Forums described delicious details:
unowned vs unowned(safe) vs unowned(unsafe)
> unowned(safe) is a non-owning reference that asserts on access that
> the object is still alive. It's sort of like a weak optional reference
> that's implicitly unwrapped with x! every time it's accessed.
> unowned(unsafe) is like __unsafe_unretained in ARC—it's a non-owning
> reference, but there's no runtime check that the object is still alive
> on access, so dangling references will reach into garbage memory.
> unowned is always a synonym for unowned(safe) currently, but the
> intent is that it will be optimized to unowned(unsafe) in -Ofast
> builds when runtime checks are disabled.
unowned vs weak
> unowned actually uses a much simpler implementation than weak.
> Native Swift objects carry two reference counts, and unowned
> references bump the unowned reference count instead of the strong
> reference count. The object is deinitialized when its strong reference
> count reaches zero, but it isn't actually deallocated until the
> unowned reference count also hits zero. This causes the memory to be
> held onto slightly longer when there are unowned references, but that
> isn't usually a problem when unowned is used because the related
> objects should have near-equal lifetimes anyway, and it's much simpler
> and lower-overhead than the side-table based implementation used for
> zeroing weak references.
Update: In modern Swift weak internally uses the same mechanism as unowned does. So this comparison is incorrect because it compares Objective-C weak with Swift unonwed.
Reasons
> What is the purpose of keeping the memory alive after owning references reach 0? What happens if code attempts to do something with > the object using an unowned reference after it is deinitialized? > > The > memory is kept alive so that its retain counts are still available. > This way, when someone attempts to retain a strong reference to the > unowned object, the runtime can check that the strong reference count > is greater than zero in order to ensure that it is safe to retain the > object. > > What happens to owning or unowned references held by the object? Is their lifetime decoupled from the object when it is deinitialized or > is their memory also retained until the object is deallocated after > the last unowned reference is released? > > All resources owned by the object are released as soon as the object's > last strong reference is released, and its deinit is run. Unowned > references only keep the memory alive—aside from the header with the > reference counts, its contents is junk.
Excited, huh?
Solution 6 - Swift
There are some great answers here. But recent changes to how Swift implements weak references should change everyone's weak self vs. unowned self usage decisions. Previously, if you needed the best performance using unowned self was superior to weak self, as long as you could be certain that self would never be nil, because accessing unowned self is much faster than accessing weak self.
But Mike Ash has documented how Swift has updated the implementation of weak vars to use side-tables and how this substantially improves weak self performance.
https://mikeash.com/pyblog/friday-qa-2017-09-22-swift-4-weak-references.html
Now that there isn't a significant performance penalty to weak self, I believe we should default to using it going forward. The benefit of weak self is that it's an optional, which makes it far easier to write more correct code, it's basically the reason Swift is such a great language. You may think you know which situations are safe for the use of unowned self, but my experience reviewing lots of other developers code is, most don't. I've fixed lots of crashes where unowned self was deallocated, usually in situations where a background thread completes after a controller is deallocated.
Bugs and crashes are the most time-consuming, painful and expensive parts of programming. Do your best to write correct code and avoid them. I recommend making it a rule to never force unwrap optionals and never use unowned self instead of weak self. You won't lose anything missing the times force unwrapping and unowned self actually are safe. But you'll gain a lot from eliminating hard to find and debug crashes and bugs.
Solution 7 - Swift
According to Apple-doc
> - Weak references are always of an optional type, and automatically > become nil when the instance they reference is deallocated. > > - If the captured reference will never become nil, it should always be captured as an unowned reference, rather than a weak reference
Example -
// if my response can nil use [weak self]
resource.request().onComplete { [weak self] response in
guard let strongSelf = self else {
return
}
let model = strongSelf.updateModel(response)
strongSelf.updateUI(model)
}
// Only use [unowned self] unowned if guarantees that response never nil
resource.request().onComplete { [unowned self] response in
let model = self.updateModel(response)
self.updateUI(model)
}
Solution 8 - Swift
If none of the above makes sense:
tl;dr
> Just like an implicitly unwrapped optional, If you can guarantee
> that the reference will not be nil at its point of use, use unowned.
> If not, then you should be using weak.
Explanation:
I retrieved the following below at: weak unowned link. From what I gathered, unowned self can't be nil but weak self can be, and unowned self can lead to dangling pointers...something infamous in Objective-C. Hope it helps
> "UNOWNED Weak and unowned references behave similarly but are NOT the same."
Unowned references, like weak references, do not increase the retain count of the object being referred. However, in Swift, an unowned reference has the added benefit of not being an Optional. This makes them easier to manage rather than resorting to using optional binding. This is not unlike Implicitly Unwrapped Optionals . In addition, unowned references are non-zeroing. This means that when the object is deallocated, it does not zero out the pointer. This means that use of unowned references can, in some cases, lead to dangling pointers. For you nerds out there that remember the Objective-C days like I do, unowned references map to unsafe_unretained references.
This is where it gets a little confusing.
> Weak and unowned references both do not increase retain counts.
They can both be used to break retain cycles. So when do we use them?!
According to Apple's docs:
> “Use a weak reference whenever it is valid for that reference to become nil at some point during its lifetime. Conversely, use an unowned reference when you know that the reference will never be nil once it has been set during initialisation.”
Solution 9 - Swift
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
let storyboard = UIStoryboard(name: "Main", bundle: nil)
let controller = storyboard.instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: "AnotherViewController")
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(controller, animated: true)
}
}
import UIKit
class AnotherViewController: UIViewController {
var name : String!
deinit {
print("Deint AnotherViewController")
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
print(CFGetRetainCount(self))
/*
When you test please comment out or vice versa
*/
// // Should not use unowned here. Because unowned is used where not deallocated. or gurranted object alive. If you immediate click back button app will crash here. Though there will no retain cycles
// clouser(string: "") { [unowned self] (boolValue) in
// self.name = "some"
// }
//
//
// // There will be a retain cycle. because viewcontroller has a strong refference to this clouser and as well as clouser (self.name) has a strong refferennce to the viewcontroller. Deint AnotherViewController will not print
// clouser(string: "") { (boolValue) in
// self.name = "some"
// }
//
//
// // no retain cycle here. because viewcontroller has a strong refference to this clouser. But clouser (self.name) has a weak refferennce to the viewcontroller. Deint AnotherViewController will print. As we forcefully made viewcontroller weak so its now optional type. migh be nil. and we added a ? (self?)
//
// clouser(string: "") { [weak self] (boolValue) in
// self?.name = "some"
// }
// no retain cycle here. because viewcontroller has a strong refference to this clouser. But clouser nos refference to the viewcontroller. Deint AnotherViewController will print. As we forcefully made viewcontroller weak so its now optional type. migh be nil. and we added a ? (self?)
clouser(string: "") { (boolValue) in
print("some")
print(CFGetRetainCount(self))
}
}
func clouser(string: String, completion: @escaping (Bool) -> ()) {
// some heavy task
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 5.0) {
completion(true)
}
}
}
> If you do not sure about [unowned self] then use [weak self]
Solution 10 - Swift
unowned is similar to weak they don't a retained object from being destroyed, but weak variables turned to nil when the object its a reference to no longer exists, which we can handle with the normal checking of nils, unowned will just become garbage, you can't tell they are no longer garbage and using them will crash. The problem with weak is if an object has references to it by weak variables, when its destroyed, it has to go through every reference to it and set that variable to nil, this clearly is going to be expensive, using unowned instead is going just crash and finding this kind of bug is going to be difficult. One place to use unowned is if you are creating some carefully contained datatype, which has a clear interface, and its internals are not directly accessible, for you implementation it may be useful to have lots of circular references but that are self contained, you can used unowned references to let you break those circular references, with out the expense of weak variables, for example you may have a node tree, and each node needs has to have a reference to its parent, deleting a node is going to delete all its children, so there is no point of all the children having to have all there parent references set to nil.